
Brand Name: PEIDE
Model Number: DYC
Place of Origin: Jiangsu, China (Mainland)
Best Hydro Pneumatic Pumping System
About the pump controlled pressurisation system
The pump controlled pressurisation system is also called the pressure maintenance system with pumps,the pressurisation system with pumps,the automatic constant pressure water supply device and pump controlled pressurisation system and vacuum deaerator. This relates to devices with or without air charging:pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank.
Operating principle of the pump controlled pressurisation system
The automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank adopt the system of static pressure as the initial design pressure head,so that the system is always under normal operating pressure.During initial operation,the make-up pump is started at first to fill the system and the bladders in the pressure tank with water,and excess water is squeezed into the bladders after the system is full.Because water is not compressible,the water chamber is continuously expanding along with the incoming water,so the air chamber is compressed, thereby causing the pressure in the tank to rise higher and higher.When the pressure reaches the set point,the make-up pump is shut off by a pressure controller.If the water in the system causes expansion so that the pressure in the system exceeds the set point,excess water will be drained off through a solenoid valve.If the water volume in the system decreases caused by a leak or temperature drop so that the pressure in the system decreases, water in the bladders is injected into the pipeline to supplement the pressure drop in the system;when the system pressure reaches the design minimum level,the make-up pump is started again by the pressure controller to inject water into the pipeline and the bladders.It goes full circle.
The fundamental functions of the automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank are to stabilize pressure and make-up water.An intelligent control system delivers proper coordination between the pump and the series of solenoid valves.Through the use of various sensors,an accurate pressure maintenence and the automatic make-up water are achieved.In addition, a fundamental function of the automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank is the obvious degassing function.Following the principles of physics,it releases water from the system into the expansion diaphragm tank for degassing,which may solve problems for water circulation.
The automatic pump controlled pressurisation system can be used with the vacuum deaerator;they are the automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & vacuum deaerator device and the automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank & vacuum deaerator device.Water which is rich in gas in the system enters into the vacuum degassing tank,and is drawn back to the system by the pump.Because water capacity is reduced in the vacuum degassing tank,gas separated out from water is expelled by an automatic exhaust valve,thereby the degassing problem in a water system is comprehensively solved.
Functions of the pump controlled pressurisation system
1. Pressure maintenence: When the temperature of a medium increases by heating,its volume expands,therefore the pressure in the whole system increases.When the opening pressure of the release solenoid valve is reached,the one in the pump controlled pressurisation system opens to release the medium expanded by the rising temperature in the system into the expansion tank to stabilize the pressure in the system.
2. Water make-up: The temperature and volume of hot water decrease after passing through the radiator,and the pressure in the system also decreases.When the pressure drops down to the starting pressure of the make-up pump,it draws water in the expansion tank or other peripheral water supply to the system in order to stabilize pressure in the system.
3.Deaerator:To degas water in the system or from the system in a vacuum,to remove solution gas,free gas,bubbles and so on,thereby protecting the pump controlled pressurisation system and allowing the system to operate in a safe and stable environment.
4. Softening: There is a water softening device (optional) in the water make-up pipe of the system,which may soften refilled water outside the system.
Outside view of the pump controlled pressurisation system
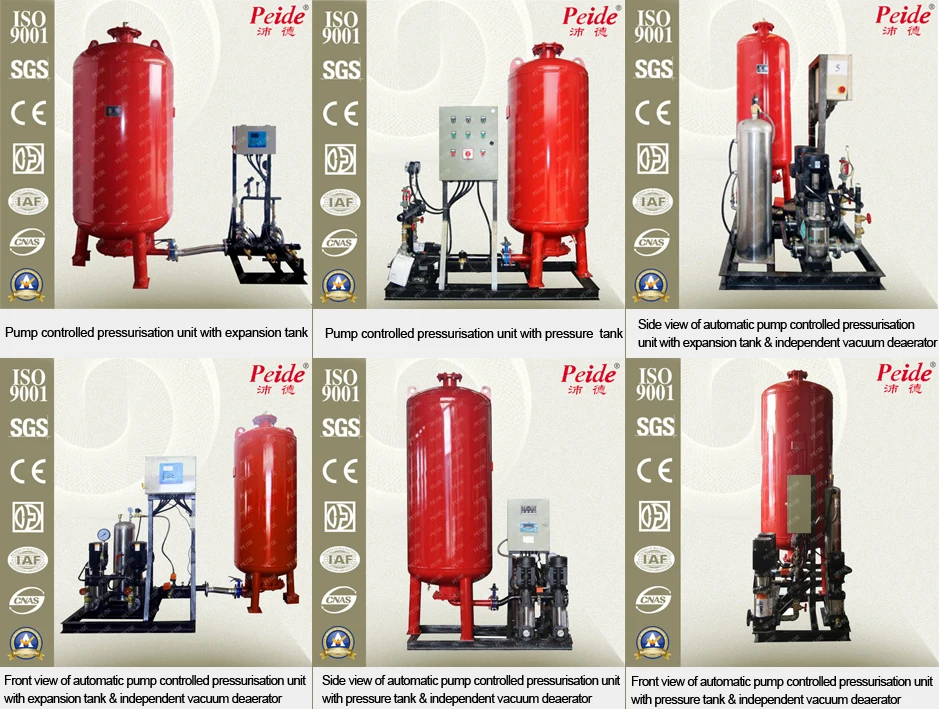

Advantages of pump controlled pressurisation system Advantages of pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank
1.High stabilizing accuracy, ±0.01mpa(±0.1bar)available.
2.Automatic water make-up,low requirements for system water make-up pressure,direct connection to the tap water system or other water supply allowable.
3.Pressure release at a set point,system safety guaranteed.
4.Total isolation of the system from the air,with no air pollution from A/C water system guaranteed.
5.Aerating once for long term use.
6.Convenient installation and use,automatic operation,safe and reliable,and easy to maintain.
Advantages of pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank
1.Use expansion tank,which is unpressurized equipment with better safety than pressure equipment.
2.The effective water capacity of the diaphragm bladder is almost equal to the total volume of the shell of the water tank,while the volume is only 1/3 of the expansion tank with the same regulating capacity.
3.No inert gases are necessary outside the diaphragm bladder,so it has better applicability,saving labor and materials.
4.The water tank adopts the bladder-type structure,pressure stabilizing force fluctuates along with expansion and shrinkage of the bladder,no direct contact between the medium and the carbon steel shell, with the result that the expansion tank remains rust-free for a prolonged period.
5.The rubber bladder volume in the expansion tank can reach more than 90% of the tank volume,with respective economies on the size and cost.
6.The system pressure can be measured by the pressure transmitter in real time.
7.The PLC intelligent control box.
8.The rubber bladder in the tank is fed from the municipal water supply system.
9.With a small floor area,convenient installation and use,fully automatic operation,safe and reliable and easy to maintain.
Advantages of the vacuum deaerator
1.Automatically degasses free gas and dissolved gas in the system.
2. The degassing efficiency and the deoxidizing efficiency is >99%.
3. Removes gases in the system to avoid air resistance,and guarantees stability and reliability during normal operation of the system.
4. Since oxygen is eliminated from the water,aerobic corrosion in the system is reduced,the service life of the pump controlled pressurisation system is prolonged.
5. Since gas is eliminated from the water,bubbles on the surface of the heat exchanger are substantially reduced,and the heat efficiency is increased.
6. The operating time and period of the deaerator can be adjusted as required.
Application range of pump controlled pressurisation system
1.The water circulation system of a heating boiler.
2.The water circulation system of an A/C for chilling.
3.The water circulation system of an A/C for cooling.
4.The heating and cooling system of a hotel,hospital,public amenity,office building and so on.
5.The closed circulation system for liquid process heating and cooling at a factory.
6.Other necessary water circulation systems.
Specification table for the pump controlled pressurisation system I. Specification table for the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank
Designation of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank
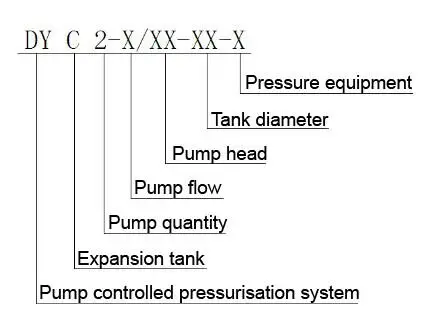
Specification table of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank
Model |
Maximum power (kw) |
Pressure equipment(bar) |
Inlet diameter(mm) |
Outlet diameter(mm) |
Length (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Height (mm) |
DYC 2-2/20-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
≥expansion tank diameter |
expansion tank height |
DYC 2-2/30-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/40-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/50-XX-10 |
1.5 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/60-XX-10 |
2.2 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/70-XX-16 |
2.2 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/90-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/110-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/150-XX-16 |
4.4 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYC 2-2/180-XX-20 |
6 |
20 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
Remark: The diameter of the expansion tank depends on its particular function.
II. Specification table for the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank
Designation of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank
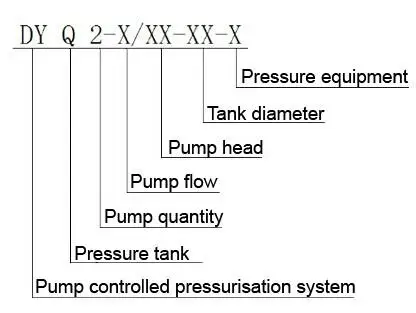
Specification table of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank
Model |
Maximum power(kw) |
Pressure equipment(bar) |
Inlet diameter(mm) |
Outlet diameter(mm) |
Length (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Height (mm) |
DYQ 2-2/20-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
≥pressure tank diameter
|
pressure tank height |
DYQ 2-2/30-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/40-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/50-XX-10 |
1.5 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/60-XX-10 |
2.2 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/70-XX-16 |
2.2 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/90-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/110-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/150-XX-16 |
4.4 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQ 2-2/180-XX-20 |
6 |
20 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
Remark: The diameter of the pressure tank depends on its particular function
III. Specification table for the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank & vacuum deaerator device
Designation of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank & vacuum deaerator device
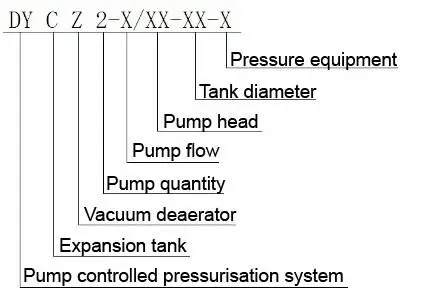
Specification table of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank & vacuum deaerator device
Model |
Maximum power (kw) |
Pressure equipment(bar) |
Inlet diameter(mm) |
Outlet diameter(mm) |
Length (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Height (mm) |
DYCZ 2-2/20-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
≥expansion tank diameter |
expansion tank height |
DYCZ 2-2/30-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/40-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/50-XX-10 |
1.5 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/70-XX-10 |
2.2 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/90-XX-16 |
2.2 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/110-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/130-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/150-XX-16 |
4.4 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
||
DYCZ 2-2/180-XX-20 |
6 |
20 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ expansion tank diameter |
Remark: The diameter of the expansion tank depends on particular case
IV.Specification table for the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & vacuum deaerator device
Designation of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & vacuum deaerator device
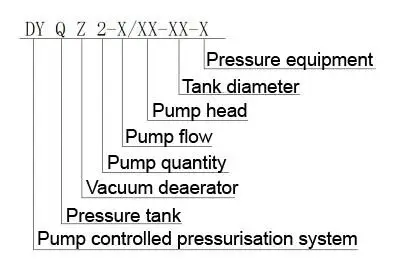
Specification table of the pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & vacuum deaerator device
Model |
Maximum power (kw) |
Pressure equipment(bar) |
Inlet diameter(mm) |
Outlet diameter (mm) |
Length (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Height (mm) |
DYQZ 2-2/20-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
≥ pressure tank diameter |
pressure tank height |
DYQZ 2-2/30-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/40-XX-6 |
1.1 |
6 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/50-XX-10 |
1.5 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/70-XX-10 |
2.2 |
10 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/90-XX-16 |
2.2 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/110-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/130-XX-16 |
3.0 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/150-XX-16 |
4.4 |
16 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
||
DYQZ 2-2/180X-X-20 |
6 |
20 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
850+ pressure tank diameter |
Remark: The diameter of the pressure tank depends on its particular function.
Installation diagram of the pump controlled pressurisation system
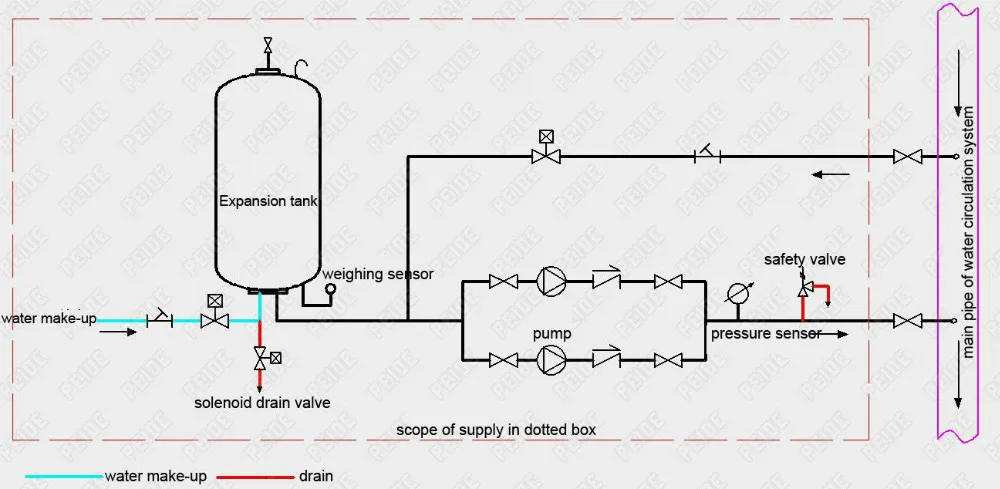
Installation diagram of automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank
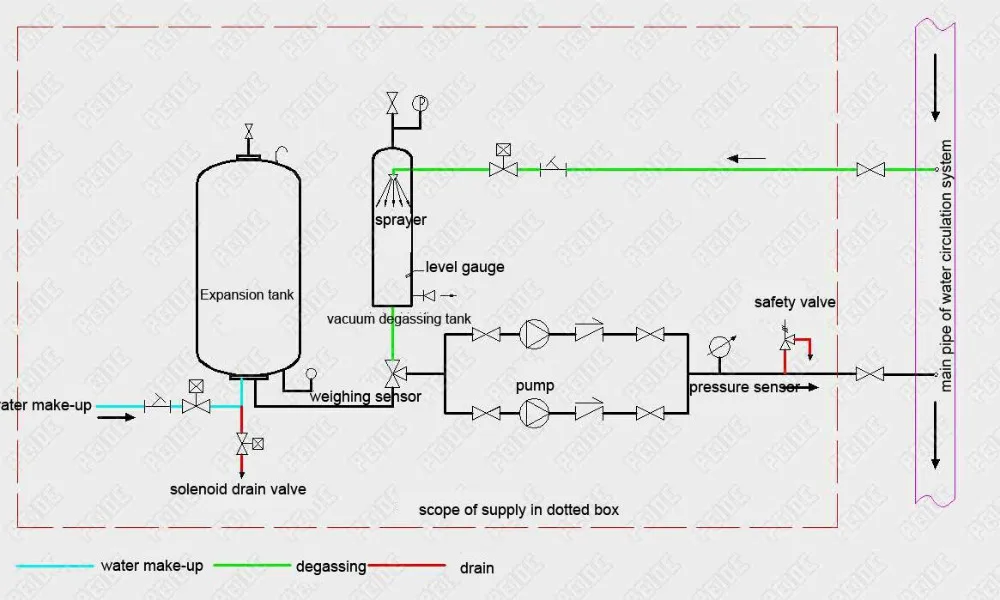
Installation diagram of automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with expansion tank & vacuum deaerator device
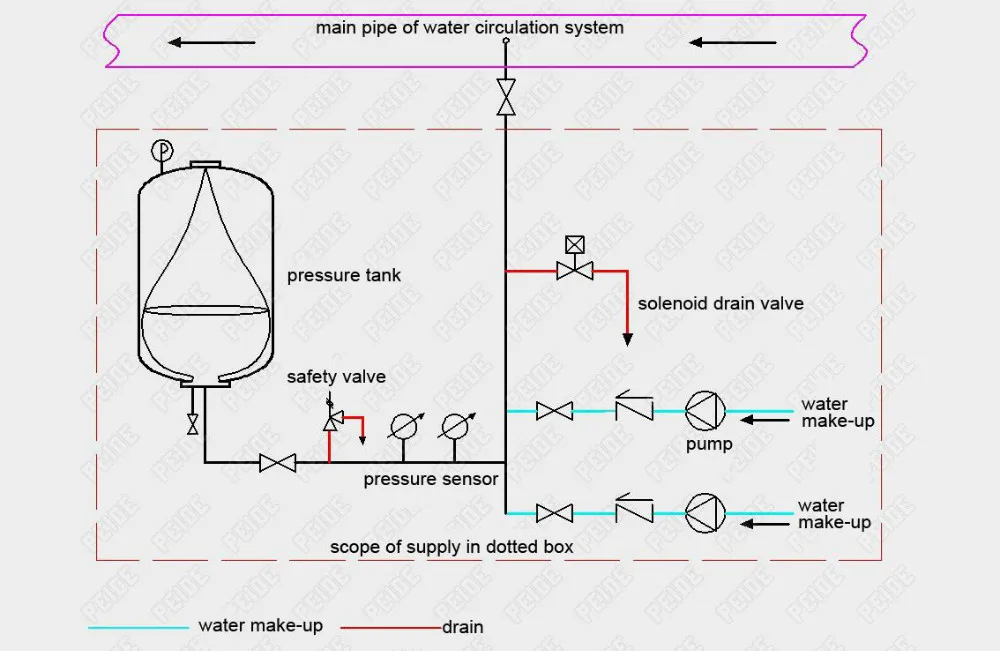
Installation diagram of automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank
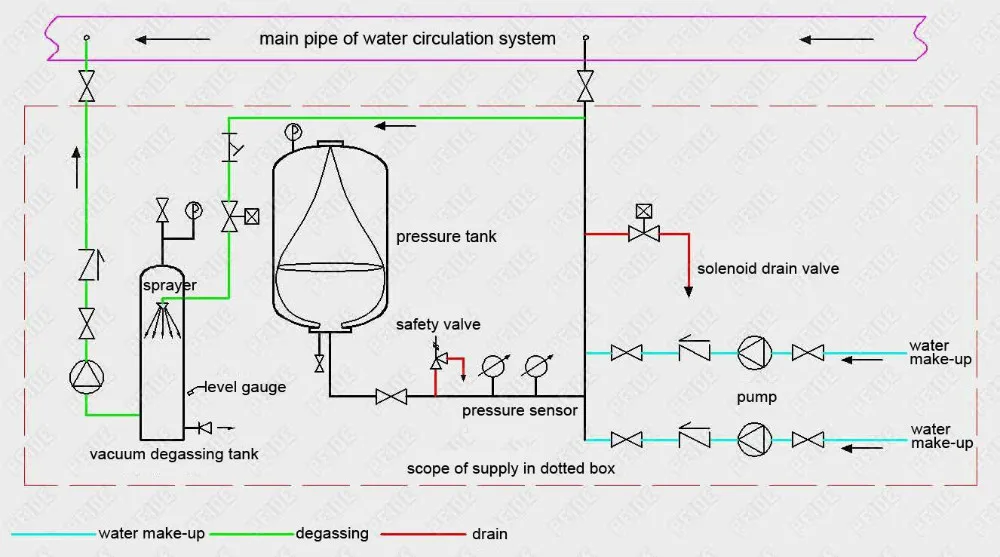
Installation diagram of automatic pump controlled pressurisation unit with pressure tank & vacuum deaerator device